|
acetochlor
Herbicide
HRAC K3 WSSA 15; chloroacetamide
NOMENCLATURE
Common name acetochlor (BSI, E-ISO, ANSI, WSSA); acétochlore ((m) F-ISO)
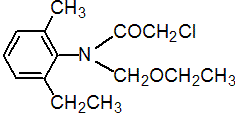
IUPAC name 2-chloro-N-ethoxymethyl-6'-ethylaceto-o-toluidide
Chemical Abstracts name 2-chloro-N-(ethoxymethyl)-N-(2-ethyl-6-methylphenyl)acetamide
CAS RN [34256-82-1] EEC no. 251-899-3 Development codes MON 097 (Monsanto)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is 92% pure. Mol. wt. 269.8 M.f. C14H20ClNO2 Form Clear viscous liquid; (tech. is a wine red to yellow or amber oil). M.p. 10.6 °C B.p. 172 ºC/5 mmHg V.p. 6.0 mPa (25 °C) KOW logP = 4.14 Henry 3.83 ´ 10-1 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.1221 (20 °C) Solubility In water 223 mg/l (25 ºC). Soluble in diethyl ether, acetone, benzene, chloroform, ethanol, ethyl acetate, and toluene. Stability Stable for over 2 years at 20 ºC (EC formulation). F.p. 160 °C (Tag closed cup)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide discovered and introduced by Monsanto Co. Manufacturers Dow AgroSciences; ÉMV; Monsanto; Nitrokémia; Sharda; Sinon; Sundat
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibits cell division by blocking protein synthesis; more recent research suggests chloroacetamides may inhibit synthesis of very long chain fatty acids (J. Schmalfuss et al., Abstr. Meeting WSSA, Toronto, 40, 117-118, 2000; P. Böger, Abstr. III Int. Weed Control Congr., Brazil 2000). Maize tolerance of chloroacetamides is due mainly to conjugation with glutathione; P450 metabolism may also be a factor. Mode of action Selective herbicide, absorbed mainly by the shoots and secondarily by the roots of germinating plants. Uses Used pre-emergence or pre-plant to control annual grasses, certain annual broad-leaved weeds and yellow nutsedge in maize (at 3 kg/ha), peanuts, soya beans, cotton, potatoes and sugar cane. Formulation types CS; EC. Selected products: mixtures: 'Degree' (+ furilazole) (Monsanto); 'Guardian' (+ furilazole) (Monsanto); 'Harness' (+ furilazole) (Monsanto); 'Acenit' (+ AD 67) (Nitrokémia); 'Erunit' (+ AD 67+ atrazine) (Nitrokémia); 'Keystone' (+ atrazine+ dichlormid) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Sacemid A' (+ TI-35) (ÉMV); 'Surpass' (+ dichlormid) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Trophy' (+ dichlormid) (Dow AgroSciences)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'TopHand' (Monsanto); 'Acetocas' (CAS); 'Curagrass' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Relay' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Sprint' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Vault' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Wenner' (Dow AgroSciences) mixtures: 'Channel' (+ furilazole) (Monsanto); 'Degree Xtra' (+ atrazine) (with safener) (Monsanto); 'Field Master' (+ atrazine+ glyphosate-isopropylammonium) (Monsanto); 'Harness Xtra' (+ atrazine) (Monsanto); 'Kadet' (+ furilazole) (Monsanto); 'Double Play' (+ EPTC) (Syngenta); 'FulTime' (+ atrazine+ dichlormid) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Racer Duo' (+ flurochloridone) (Agan); 'TopNotch' (+ dichlormid) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Trophée' (+ dichlormid) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Twin Pack Premix' (+ flurochloridone) (Agan) Discontinued products mixtures: 'Surpass 100' * (+ atrazine+ dichlormid) (Dow AgroSciences)
ANALYSIS
Product by glc. Residues by hplc. Details from Monsanto.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 2148 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits 4166 mg/kg. Contact sensitisation reactions observed in guinea pigs. Practically non-irritating to eyes and skin (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >3.0 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 11 mg/kg b.w. daily; (1 y) for dogs 2 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI 0.02 mg/kg b.w. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III EC classification Xn; R20| Xi; R37/38| R43| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 1260 mg/kg. LC50 (5 d) for quail and mallard ducks >5620 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 0.36, bluegill sunfish 1.5 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 9 mg/l. Bees LD50 (24 h) (contact) >200 mg/bee; (oral) >100 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) 211 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals The primary routes of metabolism are glutathione conjugation and metabolism by cytochrome P450. Plants In maize and soya beans, rapidly absorbed and metabolised in the germinating plant. In maize, the first metabolite is glutathione, and in soya beans homoglutathione (E. J. Breaux, J. Agric. Food Chem., 1986, 34, 884). Soil/Environment Adsorbed by soil, with little leaching. Microbial degradation accounts for most loss from soil; DT50 8-18 d.
|