|
zineb
Fungicide
FRAC M3; multi-site: alkylenebis(dithiocarbamate)
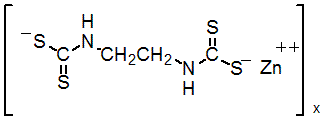
NOMENCLATURE
Common name zineb (BSI, E-ISO, JMAF); zinèbe ((m) F-ISO); no name (Germany)
IUPAC name zinc ethylenebis(dithiocarbamate) (polymeric)
Chemical Abstracts name [[1,2-ethanediylbis[carbamodithioato]](2-)]zinc
CAS RN [12122-67-7] EEC no. 235-180-1 Official codes ENT 14 874
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 275.8 M.f. C4H6N2S4Zn Form Pale yellow powder. M.p. Decomposes at 157 ºC without melting V.p. <0.01 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP £1.3 (20 ºC) Henry <2.76 ´ 10-4 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) Solubility In water c. 10 mg/l (room temperature). Practically insoluble in common organic solvents. Dissolves in some chelating agents, for example salts of ethylenediaminetetra-acetic acid, from which it cannot be recovered. Stability Unstable to light, moisture and heat on prolonged storage (decomposition is reduced by stabilisers). When precipitated from concentrated solution, a polymer is formed which is less fungicidal. F.p. 90 ºC; autoignition temperature 149 ºC
COMMERCIALISATION
History J. M. Heuberger & T. F. Manns (Phytopathology, 1943, 33, 113) reported the addition of zinc sulfate improved the field performance of nabam as a fungicide. This led to the introduction of zineb by Rohm & Haas Co. (now Dow AgroSciences), and by E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Co., (who no longer manufacture or market it). Patents US 2457674; US 3050439 Manufacturers Bayer CropScience; Cerexagri; Indofil
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Non-specific thiol reactant, inhibiting respiration. Mode of action Foliar fungicide with protective action. Uses Control of downy mildews in vines, hops, lettuce, onions, spinach, brassicas, oilseed rape, tobacco, and ornamentals; rusts in currants, berry fruit, plums, vegetables, and ornamentals (especially carnations and chrysanthemums); red fire disease on vines; potato and tomato blights; leaf spot diseases on currants, berry fruit, olives, and celery; anthracnose on beans, vines, and citrus fruit; scab on apples and pears; shot-hole on stone fruit; Cercospora on bananas; tulip fire; Botrytis; needle cast in forestry; etc. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic, except for zinc-sensitive plants such as tobacco and cucurbits. Formulation types DP; WP. Compatibility Incompatible with alkaline or mercury-containing compounds. Selected products: 'Amitan' (Sipcam); 'Indofil Z-78' (Indofil); 'Peran' (Efthymiadis); 'Phytox' (Stähler); 'Tritoftorol' (Cerexagri); 'Vitex' (Siapa); mixtures: 'Vizines' (+ sulfur) (Vipesco)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Dithane Z-78' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Sepineb' (DuPont); 'AAphytora' (Bayer CropScience); 'Azzurro' (Chemiplant); 'Bianco' (Chemiplant); 'Dipher' (Kumiai); 'Polyram-Z' (BASF); 'Zinugec' (Sipcam Phyteurop) mixtures: 'Cupro Phynebe' (+ copper oxychloride) (France) (Bayer CropScience); 'Vizincop' (+ copper oxychloride) (Vipesco) Discontinued products: 'Parzate' * (DuPont); 'Lonacol' * (Bayer) mixtures: 'Bordeaux MZ' * (+ Bordeaux mixture+ maneb) (Nufarm Americas); 'Trimanzone WP' * (+ ferbam+ maneb) (Intracrop)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by acid hydrolysis, converting the carbon disulfide evolved into dithiocarbonate which is estimated by titration with iodine (CIPAC Handbook, 1992, E, 230-235; ibid., 1998, H, 100; AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 965.15) or by liberation of arsenic which is determined spectrophotometrically (CIPAC Handbook, 1992, E, 231). Identified colorimetrically (CIPAC Handbook, 1994, F, 320) or by u.v. absorbance (ibid., p. 411). ETU content by hplc with u.v. detection, or by paper chromatography (ibid., 1994, F, 399). Determination of zinc ibid., 1994, F, 235. Residues determined by acid hydrolysis, measuring the carbon disulfide evolved using glc (Analyst (London), 1981, 106, 782) or by conversion to a copper/amine complex which is estimated by colorimetry (Pestic. Anal. Man., 1979, II; Manu. Pestic. Residue Anal., 1987, I, S21; Anal. Methods Residues Pestic., 1988, Part II; W. K. Lowen & H. L. Pease, Anal. Methods Pestic., Plant Growth Regul. Food Addit., 1964, 3, 69).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 68, 70 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). IARC ref. 12 class 3 Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5200 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >6000 mg/kg. Slight irritation of skin and mucous membranes. NOEL In feeding trials, growth was inhibited in rats within 74 w at 10 000 mg/kg diet. ADI (JMPR) 0.03 mg/kg b.w. (group ADI with mancozeb, maneb and metiram); ethylenethiourea 0.004 mg/kg b.w. [1993]. Other At very high doses, ethylenethiourea, a trace contaminant and breakdown product of zineb, has caused thyroid effects, tumours and birth defects in laboratory animals. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) IV EC classification Xi; R37| R43
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Fish LC50 for perch 2, roach 6-8 mg/l. Bees Not toxic to bees.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 78 (WHO, 1988; general review of dithiocarbamates). Plants Ethylenethiourea is the major metabolite in plants. Ethylenethiuram monosulfide and presumably ethylenethiuram disulfide and sulfur are also formed.
|