|
thiacloprid
Insecticide
IRAC 4A; neonicotinoid
NOMENCLATURE
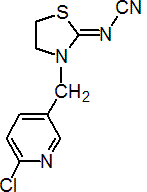
Common name thiacloprid (BSI, pa ISO)
IUPAC name (Z)-3-(6-chloro-3-pyridylmethyl)-1,3-thiazolidin-2-ylidenecyanamide
Chemical Abstracts name (Z)-[3-[(6-chloro-3-pyridinyl)methyl]-2-thiazolidinylidene]cyanamide
CAS RN [111988-49-9] Development codes YRC 2894 (Bayer)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is ³97.5% Mol. wt. 252.7 M.f. C10H9ClN4S Form Yellowish crystalline powder. B.p. decomp. >270 °C V.p. 3 ´ 10-7 mPa (20 °C) Henry 4.1 ´ 10-10 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) Solubility In water 185 mg/l (20 °C).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Reported by A. Elbert et al., (Proc. BCPC Conf. - Pests Dis., 2000, 1, 21) and developed by Bayer AG and Nihon Bayer Agrochem. First registered in Brazil in 1999. Manufacturers Bayer CropScience
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Acts as an agonist of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in the central nervous system, thus disturbing synaptic signal transmissions. Mode of action Acute contact and stomach poison, with systemic properties. Uses For use by foliar application against sucking and biting insects, at 48-216 g/ha, in pome fruit, stone fruit, small berries, cotton, vegetables, sugar beet, potatoes, rice and ornamentals. Pests controlled include aphids, whiteflies, beetles (e.g. Leptinotarsa decemlineata, Anthonomus pomorum, Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus) and Lepidoptera such as leaf miners and Cydia pomonella. Formulation types GR; SC; WG. Selected products: 'Bariard' (Bayer CropScience); 'Calypso' (Bayer CropScience)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Alanto' (Bayer CropScience)
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 836, female rats 444 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute dermal LD50 for male and female rats >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation (4 h) for male rats >2535, female rats c. 1223 mg/m3 air (aerosol). NOEL NOAEL for rats (chronic toxicity, carcinogenicity) 25 ppm. ADI 0.012 mg/kg. Other No primary carcinogenic potential; no primary developmental toxicity in rats and rabbits; no evidence of a genotoxic or mutagenic potential. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for Japanese quail 49, bobwhite quail 2716 mg/kg. LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail 5459, Japanese quail 2500 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 30.5, bluegill sunfish 25.2 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h, 20 °C) ³85.1 mg/l. Algae ErC50 (72 h, 20 °C) for Scenedesmus subspicatus 97 mg/l; EC50 for Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata >100 mg/l. Bees LD50 (oral) 17.32 mg/bee; (contact) 38.83 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d, 20 °C) for Eisenia fetida 105 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Thiacloprid was quickly and completely absorbed from the gastro-intestinal tract, followed by a fast and uniform distribution to the organs and tissues of the rat. The major portion of the administered dose was quickly eliminated with the urine and faeces. There was no indication of an accumulative behaviour in the rat. Besides the parent compound, 26 metabolites were identified in urine and faeces. In the goat, the compound was also quickly excreted, mainly with the urine. Only a very small amount was secreted with the milk.. Similarly in poultry, only a minute amount was found in the eggs. Plants Metabolism in tomatoes, apples, cotton and wheat, after spray application and in rice, after nursery box treatment, is similar in all crops. The parent compound is always the major component at harvest. Hydrolysis, oxidation and conjugation of the parent compound were the main degradation steps. Soil/Environment Soil DT50 (6 soils) 7-21 d; soil mobility (6 soils) low to medium.
|