|
profenofos
Insecticide, acaricide
IRAC 1B; organophosphate
NOMENCLATURE
Common name profenofos (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI, ESA)
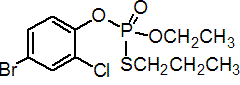
IUPAC name O-4-bromo-2-chlorophenyl O-ethyl S-propyl phosphorothioate
Chemical Abstracts name O-(4-bromo-2-chlorophenyl) O-ethyl S-propyl phosphorothioate
CAS RN [41198-08-7] EEC no. 255-255-2 Development codes CGA 15 324 (Ciba-Geigy) Official codes OMS 2004
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is ³98%. Mol. wt. 373.6 M.f. C11H15BrClO3PS Form Pale yellow liquid, with a garlic-like odour. B.p. 100 ºC/1.80 Pa V.p. 1.24 ´ 10-1 mPa (25 ºC) (OECD 104) KOW logP = 4.44 (OECD 107). Henry 1.65 ´ 10-3 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.455 (20 ºC) (OECD 109) Solubility In water 28 mg/l (25 ºC). Readily miscible with most organic solvents. Stability Relatively stable under neutral and slightly acidic conditions. Unstable under alkaline conditions; on hydrolysis, DT50 (calc.) (20 ºC) 93 d (pH 5), 14.6 d (pH 7), 5.7 h (pH 9). pKa No dissociation constant between pKa 0.6 to 12 F.p. 124 °C (EEC A9)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by F. Buholzer (Proc. Br. Insectic. Fungic. Conf., 8th, 1975, 2, 659). Introduced by Ciba-Geigy AG (now Syngenta AG). Patents BE 789937; GB 1417116 Manufacturers Agrochem; Hegang Heyou; Hesenta; Nagarjuna Agrichem; Sharda; Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. The separate optical isomers, due to the chiral phosphorus atom, show different types of insecticidal activity and ability to inhibit acetylcholinesterase (H. Leader & J. E. Casida, J. Agric. Food Chem., 1982, 30,546). Mode of action Non-systemic insecticide and acaricide with contact and stomach action. Exhibits a translaminar effect. Has ovicidal properties. Uses Control of insects (particularly Lepidoptera) and mites on cotton, maize, sugar beet, soya beans, potatoes, vegetables, tobacco, and other crops, at 250-1000 g/ha. Phytotoxicity Slight reddening of cotton may occur. Formulation types EC; UL. Selected products: 'Curacron' (Syngenta); 'Mardo' (Crop Health); 'Profex' (Nagarjuna Agrichem); 'Sanofos' (Sanonda); 'Soldier' (Devidayal)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Selecron' (Syngenta); 'Carina' (Pesticides India); 'Celcron' (Excel); 'Profex super' (Nagarjuna Agrichem); 'Seliton' (Agrochem); 'Teliton' (Agrochem) mixtures: 'Polytrin C' (+ cypermethrin) (Syngenta); 'Sirene-BW' (+ grandlure) (IPM Technologies) Discontinued products: 'Polycron' * (Ciba)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc with FID (CIPAC Handbook, 1998, H, 222). Residues determined by glc with TID. Details available from Syngenta.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 59, 61 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 358, rabbits 700 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats c. 3300, rabbits 472 mg/kg. Non-irritant to the skin and eyes of rabbits. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats c. 3 mg/l air. NOEL (using EC formulation 380 g a.i./l) for rats (2 y) 0.3 mg a.i./kg diet; for lifetime study 1.0 mg a.i./kg diet; for mice 0.08 mg/kg diet. ADI (JMPR) 0.01 mg/kg b.w. [1990]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) II EC classification Xn; R20/21/22
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail 70-200, Japanese quail >1000, mallard ducks 150-612 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 0.08, crucian carp 0.09, bluegill sunfish 0.3 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) 1.06 mg/l. Algae EC50 (72 h) for Scenedesmus subspicatus 1.16 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. Highly toxic to crustaceans. Bees LD50 (contact, 48 h) 0.102 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) 372 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 63 (WHO, 1986; a general review of organophosphorus insecticides). Animals Rats rapidly excrete 14C-profenofos after oral administration. The predominant metabolic pathway involves stepwise dealkylation and hydrolysis, followed by conjugation. Plants In cotton, Brussels sprouts and lettuce, the compound is rapidly taken up and metabolised. The overall metabolic pattern indicates degradation to polar metabolites. Soil/Environment Mean half-life in soil (lab. and field) is c. 1 week.
|