|
oxamyl
Insecticide, acaricide, nematicide
IRAC 1A; carbamate
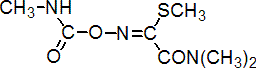
NOMENCLATURE
Common name oxamyl (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI, ESA); oxamil (JMAF)
IUPAC name N,N-dimethyl-2-methylcarbamoyloxyimino-2-(methylthio)acetamide
Chemical Abstracts name methyl 2-(dimethylamino)-N-[[(methylamino)carbonyl]oxy]-2-oxoethanimidothioate
CAS RN [23135-22-0] EEC no. 245-445-3 Development codes DPX-D1410 (DuPont)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 219.3 M.f. C7H13N3O3S Form Colourless crystals, with a garlic-like odour. M.p. At 100-102 ºC, changes to a dimorphic form which melts at 108-110 ºC B.p. Decomposes on distillation V.p. 0.051 mPa (25 °C) KOW logP = -0.44 (pH 5) Henry 3.9 ´ 10-8 Pa m3 mol-1 S.g./density 0.97 at 25 ºC Solubility In water 280 g/l (25 ºC). In methanol 1440, ethanol 330, acetone 670, toluene 10 (all in g/kg, 25 ºC). Stability Solid and formulations are stable; aqueous solutions decompose slowly; DT50 >31 d (pH 5), 8 d (pH 7), 3 h (pH 9); accelerated by aeration and sunlight.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Introduced by E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Co. 'Vydate' was first sold in 1974. Patents US 3530220; US 3658870 Manufacturers DuPont
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Contact and systemic insecticide, acaricide, and nematicide. Absorbed by the foliage and roots, with translocation (C. A. Peterson et al., Pestic. Biochem. Physiol., 1978, 8,1). Uses Control of chewing and sucking insects (including soil insects, but not wireworms), spider mites, and nematodes in ornamentals, fruit trees, vegetables, cucurbits, beet, bananas, pineapples, peanuts, cotton, soya beans, tobacco, potatoes and other crops. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic when used as directed. Some strawberry varieties may be injured. Formulation types GR; SL. Compatibility Incompatible with alkaline materials. Selected products: 'Vydate' (DuPont)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc (R. F. Holt & R. E. Leitch, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1978. 10, 111). Residues determined by glc with FPD (idem, ibid.; Man. Pestic. Residue Anal., 1987, I, 6; Anal. Methods Residues Pestic., 1988, Part I, M13; A. Ambrus et al., J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1981, 64, 733) or by rplc (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 985.23). In drinking water, by rplc and fluorimetry of liberated methylamine (ibid., 991.06).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 44, 46 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 3.1, female rats 2.5 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for male rabbits 5027, female rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Not irritating to skin, not a skin sensitiser on guinea pigs. Inhalation LC50 (1 h) (atomised spray) for male rats 0.17, female rats 0.12 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 50 mg a.i./kg diet; for dogs 50 mg/kg diet. ADI (JMPR) 0.03 mg/kg b.w. [1985]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) Ib; EPA (formulation) I EC classification T+; R26/28| Xn; R21| N; R51, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for male mallard ducks 3.83, female mallard ducks 3.16 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail 340, mallard ducks 766 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 5.6, goldfish 27.5, rainbow trout 4.2 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.319 mg/l. Algae EC50 (72 h) 3.3 mg/l (tech.). Bees Toxic to bees; LD50 (oral) 0.078-0.11 mg/bee (as 'Vydate'); (contact) 0.27-0.36 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) 112 ppm.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 64 (WHO, 1986; a review of carbamate insecticides in general). Animals In rats, oxamyl was hydrolysed to an oximino metabolite (methyl N-hydroxy-N',N'-dimethyl-1-thiooxamimidate) or converted enzymically via N,N-dimethyl-1-cyanoformamide to N,N-dimethyloxamic acid. Conjugates of the oximino compound, the acid, and their monomethyl derivatives constituted over 70% of the metabolites excreted in the urine and faeces (J. Harvey & J. C-Y. Han, J. Agric. Food Chem., 1978, 26, 902-910). Metabolism of carbamate insecticides is reviewed (M. Cool & C. K. Jankowski in "Insecticides"). Plants In plants, oxamyl hydrolyses to the corresponding oximino compound which, in turn, conjugates with glucose. Total breakdown into natural products has been demonstrated (J. Harveyet al., J. Agric. Food Chem., 1978, 26, 529-536). Soil/Environment Degraded rapidly in soil, DT50 c. 7 d. DT50 in groundwater (lab. study) 20 d (anaerobic), 20-400 d (aerobic) (J. H. Smelt et al., Pestic. Sci., 1983, 14, 173-181). Koc 25.
|