|
oxadixyl
Fungicide
FRAC 4, A1; phenylamide: oxazolidinone
NOMENCLATURE
Common name oxadixyl (BSI, draft E-ISO, draft F-ISO)
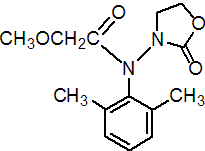
IUPAC name 2-methoxy-N-(2-oxo-1,3-oxazolidin-3-yl)aceto-2',6'-xylidide
Chemical Abstracts name N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-methoxy-N-(2-oxo-3-oxazolidinyl)acetamide
CAS RN [77732-09-3] Development codes SAN 371F (Sandoz)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 278.3 M.f. C14H18N2O4 Form Colourless, odourless crystals. M.p. 104-105 ºC V.p. 0.0033 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = 0.65-0.8 (22-24 ºC) Henry 2.70 ´ 10-7 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density Bulk density 0.5 kg/l Solubility In water 3.4 g/kg (25 ºC). In acetone 344, dimethyl sulfoxide 390, methanol 112, ethanol 50, xylene 17, diethyl ether 6 (all in g/kg, 25 ºC). Stability Stable under normal conditions, and when stored at 70 ºC for 2-4 weeks. A 20 ppm solution of the a.i. is stable in aqueous buffer solutions of pH 5, 7 and 9 at room temperature, DT50 c. 4 y.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Systemic fungicide reported by U. Gisi et al. (Meded. Fac. Landbouwwet. Rijksuniv. Gent, 1983, 48, 541). Introduced by Sandoz AG (now Syngenta AG) and first marketed in 1984. Patents GB 2058059 Manufacturers Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry It is assumed that it inhibits protein synthesis in fungi, by interference with the synthesis of ribosomal RNA. Mode of action Systemic fungicide with curative and protective action. Rapidly absorbed by the leaves and roots, with translocation principally acropetally, but also basipetally and by translaminar movement. Exhibits a synergistic effect with contact fungicides. Uses In combination with contact fungicides, for control of Peronosporales, such as downy mildews, late blights, and rusts, in vines, maize, potatoes, tobacco, hops, sunflowers, citrus, fruit and vegetables, and as a seed dressing on cotton, peas and sunflowers. Application rates for foliar use, 200-300 g/ha. Formulation types FG; WG; WP. Selected products: 'Anchor' (Gustafson); mixtures: 'Pulsan' (+ cymoxanil+ mancozeb) (Syngenta); 'Sandofan' (+ mancozeb) (Syngenta)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Blason' (Syngenta) mixtures: 'Apron Elite' (+ thiram+ carbendazim+ cymoxanil) (Syngenta); 'Recoil' (+ mancozeb) (Syngenta); 'Ripost' (+ cymoxanil+ mancozeb) (Syngenta); 'Wakil' (+ thiram+ carbendazim+ cymoxanil) (Syngenta); 'Sirdate P' (+ cymoxanil+ maneb) (Griffin); 'Sirdate S' (+ cymoxanil+ folpet) (DuPont); 'Trustan' (+ cymoxanil+ mancozeb) (DuPont)
ANALYSIS
By rp hplc with u.v. detection (CIPAC Handbook, 1995, G, 122-127) or by glc with TSD; details available from Syngenta.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 3480, female rats 1860 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats and rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits), nor a skin sensitiser to guinea pigs. Inhalation LC50 (6 h) for male and female rats >5.6 mg/l air. NOEL (1 y) for dogs 500 mg/kg diet; (90 d and lifetime) for rats 250 mg/kg diet. Not teratogenic in rabbits (up to 200 mg/kg b.w. daily) or rats (up to 1000 mg/kg b.w. daily) and no significant effect on reproduction in rats (up to 1000 mg/kg diet). Other Acute i.p. LD50 for male rats 490, female rats 550 mg/kg. Not mutagenic in the Ames, micronucleus and other standard assays. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) III EC classification (Xn; R22)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks >2510 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducks and Japanese quail >5620 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for carp >300, rainbow trout >320, bluegill sunfish 360 mg/l. Does not bioaccumulate in fish. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 530 mg/l. Algae IC50 for Scenedesmus subspicatus 46 mg/l. Bees LD50 (oral) >200 mg/bee; (contact) >100 mg/bee. Worms LD50 (14 d) for earthworms >1000 ppm (mg a.i./kg dry soil).
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In rats, following oral administration, absorption is rapid and almost complete, with 81-92% eliminated within 144 hours, in the urine and faeces. Extensive metabolism occurs, mainly by hydrolysis at various points on the methoxyacetamide moiety, and oxidation of the methyl group on the phenyl ring to the corresponding alcohol. Similar metabolites are found in soil and in plants. Plants In plants, the major part (>94%) of the applied dosage remains unchanged. A maximum of 9% penetrates the leaf surface after 42 days, and c. 42% of this is metabolised. Soil/Environment In laboratory experiments, DT50 was 6-9 mo. However, in the field, DT50 values of 2-3 mo were observed. In soil, the main metabolite is oxadixyl acid.
|