|
omethoate
Insecticide, acaricide
IRAC 1B; organophosphate
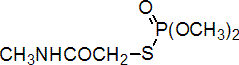
NOMENCLATURE
Common name omethoate (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO); no name (Italy)
IUPAC name O,O-dimethyl S-methylcarbamoylmethyl phosphorothioate
Chemical Abstracts name O,O-dimethyl S-[2-(methylamino)-2-oxoethyl] phosphorothioate
CAS RN [1113-02-6] EEC no. 214-197-8 Development codes Bayer 45 432; S 6876 (Bayer)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 213.2 M.f. C5H12NO4PS Form Colourless liquid, with a mercaptan odour. M.p. Solidifies -28 °C (tech.) B.p. Decomposes at c. 135 ºC V.p. 3.3 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = -0.74 (20 ºC) S.g./density 1.32 (20 ºC) Solubility Readily soluble in water, alcohols, acetone, and many hydrocarbons. Slightly soluble in diethyl ether. Almost insoluble in petroleum ether. Stability Hydrolysed in alkaline media; relatively slowly hydrolysed in acidic media: DT50 (est.) 102 d (pH 4), 17 d (pH 7), 28 h (pH 9) (22 ºC). F.p. 128 °C (tech.)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by R. Santi & P. de Pietri-Tonelli (Nature (London), 1959, 183, 398). Introduced by Bayer AG. Patents DE 1251304 Manufacturers Bayer CropScience
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Systemic insecticide and acaricide with contact and stomach action. Uses Control of spider mites, aphids (including woolly aphids), beetles, caterpillars, scale insects, thrips, suckers, frit flies, etc. on fruit, hops, cereals, rice, potatoes, ornamentals, and other crops. Application rates vary from 35 to 1000 g/ha, depending on crop, pest, pest stage and application method. Phytotoxicity May be phytotoxic to some varieties of peach. Formulation types AE; EC; SL; UL. Compatibility Incompatible with alkaline materials. Selected products: 'Folimat' (Bayer CropScience)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Dimethoxon' (BASF); 'Le-mat' (Bayer CropScience)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by rp hplc or by glc with FPD (CIPAC Handbook, 1992, E, 159-162). In dimethoate, ibid., 1998, H, 157. Residues determined by glc with FID (Man. Pestic. Residue Anal., 1987, I, 6, S13, S17, S19; Anal. Methods Residues Pestic., 1988, Part I, M2, M5, M12; Analyst (London), 1977, 102, 858; AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 985.22). Details available from Bayer CropScience.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 77(see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats c. 25 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 (24 h) for male rats 232, female rats c. 145 mg/kg. Not irritating to the skin; slightly irritating to the eyes (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats c. 0.3 mg/l (aerosol). NOEL NOAEL (2 y) for rats 0.3, mice 10 ppm. NOEL (1 y) for dogs 0.025 mg/kg b.w. ADI (JMPR) ADI withdrawn [1996]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) Ib; EPA (formulation) I EC classification T; R25| Xn; R21| N; R50
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for male Japanese quail 79.7, female Japanese quail 83.4 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for golden orfe 30, rainbow trout 9.1 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.022 mg/l. Algae ErC50 for Scenedesmus subspicatus 167.5 mg/l. Bees Toxic to bees. Worms LC50 for Eisenia foetida 46 mg/kg dry soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 63 (WHO, 1986; a general review of organophosphorus insecticides). Animals Omethoate is not accumulated in animal tissues or fat. The main metabolites in the urine are O-demethylomethoate and N-methyl-2-(methyldithio)acetamide. Plants Omethoate is rapidly taken up by plants. Demethylation and hydrolysis of P-S bonds are the main metabolic steps. The main metabolites are 3-hydroxy-3-[(2-methylamino-2-oxo-ethyl)thio]propionic acid and its oxidation products. Soil/Environment Omethoate has a relatively high mobility in soil but is very rapidly metabolised; DT50 only a few days. The main metabolite is CO2. Aged leaching studies revealed that metabolites have only a low leaching potential.
|