|
methomyl
Insecticide, acaricide
IRAC 1A; carbamate
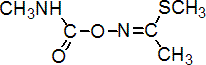
NOMENCLATURE
Common name methomyl (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI, ESA, JMAF)
IUPAC name S-methyl N-(methylcarbamoyloxy)thioacetimidate
Chemical Abstracts name methyl N-[[(methylamino)carbonyl]oxy]ethanimidothioate
CAS RN [16752-77-5] EEC no. 240-815-0 Development codes DPX-X1179 (DuPont) Official codes OMS 1196
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Methomyl is a mixture of (Z)- and (E)- isomers, the former predominating. Mol. wt. 162.2 M.f. C5H10N2O2S Form Colourless crystals, with a slight sulfurous odour. M.p. 78-79 ºC V.p. 0.72 mPa (25 °C) KOW logP = 0.093 Henry 2.13 ´ 10-6 Pa m3 mol-1 S.g./density 1.2946 (25 ºC) Solubility In water 57.9 g/l (25 ºC). In methanol 1000, acetone 730, ethanol 420, isopropanol 220, toluene 30 (all in g/kg, 25 ºC). Sparingly soluble in hydrocarbons. Stability Stable in water for 30 d (pH 5 and 7); DT50 c. 30 d (pH 9). Stable up to 140 ºC. Stable to sunlight when exposed for 120 d.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by G. A. Roodhans & N. B. Joy (Meded. Rijksfac. Landbouwwet. Gent, 1968, 33, 833). Introduced by E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Co. 'Lannate' was first marketed in 1967. Patents US 3576834; US 3639633 Manufacturers Bayer CropScience; CAC; Crystal; Dow AgroSciences; DuPont; Hunan Linxiang; Jiangsu Eternal; Kuo Ching; Makhteshim-Agan; Rotam; Sinon
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Systemic insecticide and acaricide with contact and stomach action. Uses Control of a wide range of insects (particularly Lepidoptera, Hemiptera, Homoptera, Diptera and Coleoptera) and spider mites in fruit, vines, olives, hops, vegetables, ornamentals, field crops, cucurbits, flax, cotton, tobacco, soya beans, etc. Also used for control of flies in animal and poultry houses and dairies. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic when used as recommended, except to some varieties of apple. Formulation types SL; SP; WP. Selected products: 'Lannate' (DuPont); 'Agrinate' (Vapco); 'Arizona' (Rocca); 'Avance' (Cequisa); 'Dimethilin' (Efthymiadis); 'Dunet' (Dhanuka); 'Kuik' (Rotam); 'Lann WDK' (Trithin); 'Matador' (Ingeniería Industrial); 'Methomex' (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Methosan' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Nudrin' (BASF); 'Pilarmate' (Pilarquim); 'Sathomyl' (Sanonda)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Kipsin' (Bayer CropScience); 'Lanox' (Crystal); 'Methavin' (Bayer CropScience); 'Tomilo' (Aragro) mixtures: 'Flybait' (+ muscalure) (Denka); 'Goldben' (+ muscalure) (public health) (Vapco); 'Golden Malrin Fly Bait' (+ muscalure) (Novartis A H); 'Last Dream PBW' (+ chlorpyrifos+ gossyplure) (Troy Biosciences); 'Methofan' (+ endosulfan) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Metofan forte' (+ endosulfan) (Aragro); 'Sepiclar T' (+ tetradifon) (Griffin); 'Stimukil' (+ muscalure) (Troy Biosciences) Discontinued products: 'Halvard' * (Shell)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc (CIPAC Handbook, 1998, H, 199; AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 995.14, J. E. Thean et al., J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1978, 61, 15; R. E. Leitch & H. L. Pease, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1973, 7, 331). Residues determined by glc with FPD (idem, ibid.; R. T. Krause, J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1980, 63, 1114; M. A. Luke et al., ibid., 1981, 64, 1187; A. Ambrus et al., ibid., p. 733) or by rplc (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 985.23). Details available from DuPont. In drinking water, by rplc and fluorimetry of liberated methylamine (ibid., 991.06).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 92, 94 (see part 2 of Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 34, female rats 30 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for male and female rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Mild eye irritant (rabbits). Not a skin irritant (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats 0.3 mg/l air (aerosol). NOEL (2 y) for rats 100, mice 50, dogs 100 mg/kg diet. ADI (JMPR) 0.02 mg/kg b.w. [2001]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) Ib; EPA (formulation) I, IV EC classification T+; R28| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks 15.9, pheasants 15.4 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for Pekin ducks 1890, bobwhite quail 3680 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 3.4, bluegill sunfish 0.9 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 31.7 mg/l. Algae EC50 (72 h) 60 mg/l. Bees Toxic to bees, contact LD50 0.1 mg/bee, but not hazardous when the spray has dried. Worms LC50 (14 d) 23 mg/kg dry soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 178 (WHO, 1996). Methomyl Health & Safety Guide: 97 (WHO 1995). Animals In rats, methomyl was rapidly converted to methomyl methylol, oxime, sulfoxide and sulfoxide oxime; these unstable intermediates were converted to acetonitrile and CO2, which were eliminated primarily via respiration and in the urine. Metabolism of carbamate insecticides is reviewed (M. Cool & C. K. Jankowski in "Insecticides"). Plants DT50 following leaf application c. 3-5 d. Rapidly degraded to CO2 and acetonitrile, with incorporation into natural plant components (J. Harvey & R. W. Reiser, Agric. Food Chem., 1973, 21, 775). Soil/Environment Rapidly degraded in soil. DT50 4-8 d at 20°C and soil moisture pF 2-2.5 in soils with pH from 5.1 to 7.8 and 1.2 to 3.6 % o.m. DT50 in groundwater samples <0.2 d (J. H. Smelt, Pestic. Sci., 1983, 14, 173-181). Koc 72.
|