|
imazaquin
Herbicide
HRAC B WSSA 2; imidazolinone
NOMENCLATURE
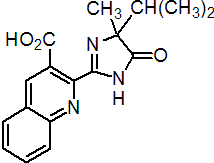
imazaquin
Common name imazaquin (BSI, ANSI, draft E-ISO, WSSA); imazaquine ((m) draft F-ISO)
IUPAC name (RS)-2-(4-isopropyl-4-methyl-5-oxo-2-imidazolin-2-yl)quinoline-3-carboxylic acid
Chemical Abstracts name (?-2-[4,5-dihydro-4-methyl-4-(1-methylethyl)-5-oxo-1H-imidazol-2-yl]-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid
CAS RN [81335-37-7] unstated stereochemistry Development codes AC 252 214; CL 252 214 (both Cyanamid); BAS 725 01H (BASF)
imazaquin-ammonium
IUPAC name ammonium (RS)-2-(4-isopropyl-4-methyl-5-oxo-2-imidazolin-2-yl)quinoline-3-carboxylate
Chemical Abstracts name ammonium (?-2-[4,5-dihydro-4-methyl-4-(1-methylethyl)-5-oxo-1H-imidazol-2-yl]-3-quinolinecarboxylate
CAS RN [81335-47-9] unstated stereochemistry Development codes BAS 725 03H (BASF)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
imazaquin
Composition Tech. is >95% pure. Mol. wt. 311.3 M.f. C17H17N3O3 Form Tan solid, with slightly pungent odour. M.p. 219-224 ºC (decomp.) V.p. <0.013 mPa (60 ºC) KOW logP = 0.34 (pH 7, 22 ºC) Solubility In water 60-120 mg/l (25 ºC). In toluene 0.4, dimethylformamide 68, dimethyl sulfoxide 159, dichloromethane 14 (all in g/l, 25 ºC). Stability Stable for 3 months at 45 ºC, 2 y at room temperature when stored in the dark. Rapidly degraded on exposure to u.v. light. pKa 3.8
imazaquin-ammonium
Mol. wt. 328.4 M.f. C17H20N4O3 Solubility In water 160 g/l (pH 7, 20 °C). Stability Hydrolysis DT50 >30 d (ARS PPD).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by P. L. Orwick et al. (Abstr. 1983 Weed Sci. Soc. Annu. Mtg., 36th, 1983, pp. 90, 91), P. K. Martin (ibid., p. 90, No. 46) and H. M. Hackworth et al. (ibid., p. 91). Introduced by American Cyanamid Co. (now BASF AG); registered in US in 1986. Patents US 4798619 Manufacturers BASF; Milenia; Shenyang
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Blocks biosynthesis of branched chain amino acids valine, leucine, and isoleucine through inhibition of acetohydroxy acid synthase, thus causing disruption of protein synthesis, which leads to interference in DNA synthesis and cell growth (D. L. Shaner et al., Plant Physiol., 1984, 76, 545). Selectivity in soya beans is attributed to rapid detoxification via ring-opening (B. Tecle et al., Proc. 1997 Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 2,605). Mode of action Selective systemic herbicide, absorbed by the roots and foliage, with translocation in the xylem and phloem throughout the plant, and accumulation in the meristematic regions. Uses Pre-planting, pre-emergence or early post-emergence control of broad-leaved weeds in soya beans, at 70-140 g a.e./ha. Also controls or reduces competition from grasses and sedges. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic to soya beans. Formulation types WG.
imazaquin
Compatibility Compatible with soil-applied grass herbicides. If mixed with post-emergence grass herbicides, reduced activity against grasses will result due to herbicide antagonism. Selected products: 'Scepter 70' (BASF); 'Topgan' (Makhteshim-Agan, Milenia) Formulation types SL.
imazaquin-ammonium
Selected products: 'Scepter' (BASF)
OTHER PRODUCTS
imazaquin
Mixtures: 'Backdraft' (+ glyphosate-isopropylammonium) (BASF); 'Steel' (+ imazethapyr+ pendimethalin) (BASF) Discontinued products mixtures: 'Structure' * (+ imazethapyr+ pendimethalin) (BASF)
imazaquin-ammonium
'Image' (BASF) mixtures: 'Chekway' (+ pendimethalin) (BASF); 'Concord' (+ chlormequat chloride+ ethephon) (BASF); 'Detail' (+ dimethenamid) (BASF); 'Meteor' (+ chlormequat chloride) (BASF); 'Mondium' (+ chlormequat chloride) (BASF); 'One Shot' (+ glyphosate-isopropylammonium) (BASF); 'Satellite' (+ chlormequat chloride+ ethephon) (BASF); 'Squadron' (+ pendimethalin) (BASF); 'Tri-Scept' (+ trifluralin) (BASF) Discontinued products: 'Tone-up' * (BASF) mixtures: 'Scepter OT' * (+ acifluorfen-sodium) (BASF)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
imazaquin
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male and female rats >5000, female mice 2363 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for male and female rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to eyes; mildly irritating to skin (rabbits). No skin sensitisation (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >5.7 mg/l air. NOEL (90 d) for rats 10 000 mg/kg diet; (2 y) for rats 5000 mg/kg. ADI 0.25 mg/kg b.w. Other Non-carcinogenic, non-mutagenic and non-teratogenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) III
ECOTOXICOLOGY
imazaquin
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >2150 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5000 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for channel catfish 320, bluegill sunfish 410, rainbow trout 280 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 280 mg/l. Algae EC50 for Selenastrum 19, for Anabaena 0.09 mg/l. Bees Contact LD50 for honeybees >100 mg/bee. Worms LC50 >23.5 mg/kg soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Imazaquin is metabolically inert in rats. Following oral administration, almost all was excreted in the urine as the unchanged compound within 2 days. No accumulation in blood or tissues. Plants Rapidly metabolised by soya bean plants to inactive compounds, formed by opening of the imidazolinone ring at the ring amide (D. L. Shaner & P. A. Robson, Weed Sci., 1985, 33, 469). Soil/Environment Steadily degraded in soil by microbial activity and photolysis, but may remain active in the soil for several weeks to several months, depending on environmental conditions (G. Basham et al., Weed Sci., 1987, 35, 576). DT50 60 d; Koc 20.
|