|
glufosinate-ammonium
Herbicide
HRAC H WSSA 10; phosphinic acid
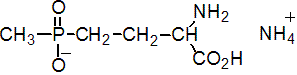
NOMENCLATURE
glufosinate-ammonium
IUPAC name ammonium 4-[hydroxy(methyl)phosphinoyl]-DL-homoalaninate; ammonium DL-homoalanin-4-yl(methyl)phosphinate
Chemical Abstracts name ammonium (?-2-amino-4-(hydroxymethylphosphinyl)butanoate
CAS RN [77182-82-2] unstated stereochemistry EEC no. 278-636-5 Development codes AE F039866 (AgrEvo); Hoe 039866 (Hoechst)
glufosinate
Common name glufosinate (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI)
IUPAC name 4-[hydroxy(methyl)phosphinoyl]-DL-homoalanine; DL-homoalanin-4-yl(methyl)phosphinic acid
Chemical Abstracts name (?-2-amino-4-(hydroxymethylphosphinyl)butanoic acid
Other names phosphinothricin (L-isomer) CAS RN [53369-07-6] racemate; [51276-47-2] unstated stereochemistry; [35597-44-5] (formerly [121783-99-1], [125604-94-6]) L-isomer Development codes AE F035956 (AgrEvo)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
glufosinate-ammonium
Mol. wt. 198.2 M.f. C5H15N2O4P Form Crystalline solid, with a slightly pungent odour. M.p. 215 ºC V.p. <0.1 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP <0.1 (pH 7, 22 ºC) Henry 4.48 ´ 10-9 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.4 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 1370 g/l (22 ºC). In acetone 0.16, ethanol 0.65, ethyl acetate 0.14, toluene 0.14, hexane 0.2 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Stable to light.
glufosinate
Mol. wt. 181.1 M.f. C5H12NO4P V.p. Low pKa pKa1 <2, pKa2 2.9, pKa3 9.8
COMMERCIALISATION
History The ammonium salt was reported as a herbicide by F. Schwerdtle et al. (Z. Pflanzenkr. Pflanzenschutz, 1981, Sonderheft IX, p. 431) and was introduced by Hoechst AG (now Bayer CropScience). Manufacturers Bayer CropScience
APPLICATIONS
glufosinate-ammonium
Biochemistry Glutamine synthetase inhibitor; leads to accumulation of ammonium ions, and inhibition of photosynthesis. Mode of action Non-selective contact herbicide with some systemic action. Translocation occurs only within leaves, predominantly from the leaf base to the leaf tip. Uses Glufosinate-ammonium is used for control of a wide range of annual and perennial broad-leaved weeds and grasses in fruit orchards, vineyards, rubber and oil palm plantations, ornamental trees and bushes, non-crop land, and pre-emergence in vegetables. Also used as a desiccant in potatoes, sunflowers, etc. For control of annual and perennial weeds and grasses in glufosinate-tolerant crops (oilseed rape, maize, soya beans, sugar beet) developed through gene technology. Applied at 0.4-1.5 kg/ha. Formulation types SL. Compatibility Compatible with diuron, simazine, MCPA, and some other herbicides. Selected products: 'Basta' (Bayer CropScience); 'Liberty' (Bayer CropScience)
OTHER PRODUCTS
glufosinate-ammonium
'Buster' (Bayer CropScience); 'Challenge' (Bayer CropScience); 'Conquest' (Bayer CropScience); 'Dash' (Bayer CropScience); 'Derringer F' (Bayer CropScience); 'Eagle' (Bayer CropScience); 'Finale' (Bayer CropScience); 'Harvest' (Bayer CropScience); 'Ignite' (Bayer CropScience); 'Rely' (Bayer CropScience); 'Remove' (Bayer CropScience); 'Touchweed' (Nomix-Chipman) mixtures: 'Groundboy' (+ flumioxazin) (Sumitomo); 'Liberty ATZ' (+ atrazine) (Bayer CropScience)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc with u.v. determination (CIPAC Handbook, 1995, G, 89-93). Details available from Bayer CropScience. Residue analysis by glc after derivatisation (Man. Pestic. Residue Anal. DFG651).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
glufosinate-ammonium
Reviews FAO/WHO 86, 88 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). E. Ebert et al., Fd. Chem. Toxic.,28(5), 339-349 (1990); R. Hack et al., Fd. Chem. Toxic., 32(5), 461-470 (1994). Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 2000, female rats 1620, male mice 431, female mice 416, dogs 200-400 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for male rats >4000, female rats c. 4000 mg/kg. Not a skin or eye irritant. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for male rats 1.26, female rats 2.60 mg/l air (dust); for rats >0.62 mg/l air (aerosol). NOEL (2 y) for rats 2 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI (JMPR) 0.02 mg/kg b.w. (for glufosinate-ammonium, N-acetylglufosinate and 3-methylphosphinico-propionic acid, alone, or in combination) [1999]. Other No teratogenic, carcinogenic, mutagenic or neurotoxic effects have been observed. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) III EC classification Xn; R22
ECOTOXICOLOGY
glufosinate-ammonium
Birds Dietary LC50 (8 d) for Japanese quail >5000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 710, carp, bluegill sunfish, golden orfe >1000 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 560-1000 mg/l. Algae LD50 for Scenedesmus subspicatus ³1000, Selenastrum capricornutum 37 mg/l. Bees Not hazardous to bees; LD50 >100 mg/bee. Worms LD50 for earthworms >1000 mg/kg soil. Other beneficial spp. Not toxic to beneficial arthropods.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Rapidly excreted, predominantly via faeces (90%). The principal metabolite is 3-(methyl)phosphinoylpropionic acid. A further faecal metabolite is N-acetylglufosinate, formed by intestinal micro-organisms. Plants Non-selective use: only the metabolite, 3-(methyl)phosphinoylpropionic acid (3-MPP), is taken up in traces from the soil. Desiccation: most of the residues consist of parent glufosinate-ammonium, with minor amounts of metabolite 3-MPP. Selective use: the principal metabolite is N-acetylglufosinate, with lesser amounts of parent and 3-MPP. Soil/Environment Rapidly degraded in surface levels of soil, and in water. Because of polarity, it and its metabolites do not bioaccumulate. Metabolism in soil and water reviewed (E. Dorn et al., Z. Pflanzenkr. Pflanzenschutz, 1992, Sonderheft XIII, pp. 459-468). Degraded to 3-(methyl)phosphinoylpropionic acid and 2-(methyl)phosphinoylacetic acid, and ultimately to CO2 and bound residues. In soil, DT50 3-10 d (lab.), 7-20 d (field); DT90 10-30 d (lab.); DT50 of metabolites 7-19 d (lab.). DT50 in water c. 2-30 d. Lysimeter studies and model calculations show that neither a.i. nor metabolites leach into groundwater; this appears to be due to rapid degradation, and adsorption to certain soil elements. Adsorption is more correlated with clay content than organic matter, Kclay 2-115, Koc 10-1230. (A. Zumdick et al., Proc. 9th IUPAC Int. Congr. Pestic. Chem., London, 1998, 2, 6A-023; idem, ibid., 6D-034).
|