|
fosetyl-aluminium
Fungicide
FRAC 33; phosphonate
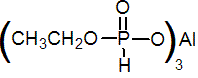
NOMENCLATURE
fosetyl-aluminium
Common name fosetyl-aluminium
IUPAC name aluminium tris-O-ethylphosphonate
Other names efosite-Al* (rejected common name proposal); EPAL CAS RN [39148-24-8] EEC no. 254-320-2 Development codes LS 74 783; RP 32545 (both Rhône-Poulenc)
fosetyl
Common name fosetyl (BSI, draft E-ISO, (m) draft F-ISO (since 1984)); phosethyl* ((m) draft F-ISO (before 1984))
IUPAC name ethyl hydrogen phosphonate
Chemical Abstracts name ethyl hydrogen phosphonate
Other names efosite* (rejected common name proposal) CAS RN [15845-66-6]
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
fosetyl-aluminium
Composition Tech. is ³95% pure. Mol. wt. 354.1 M.f. C6H18AlO9P3 Form Colourless powder; (tech. is a white to yellowish powder). M.p. 215 °C V.p. <10-4 mPa (25 °C) KOW logP = -2.1 to -2.7 (23 °C) Henry <3.24 ´ 10-5 Pa m3 mol-1 (20 °C, calc.) Solubility In water 111.3 g/l (pH 6, 20 ºC). In methanol 920, acetone 13, ethyl acetate <1 (all in mg/l, 20 ºC). Stability Hydrolysis of fosetyl-aluminium occurs under extreme acid or alkaline conditions. DT50 5 d (pH 3), 13.4 d (pH 13). Decomposes above 276 ºC. Photostability DT50 23 daylight hours. pKa 4.7 (20-25 °C)
fosetyl
Mol. wt. 110.0 M.f. C2H7O3P
COMMERCIALISATION
History Fungicidal activity of aluminium salt reported by D. Horrière et al. (Phytiatr.-Phytopharm., 1977, 26, 3). Fosetyl-aluminium was introduced by Rhône-Poulenc Agrochimie (now Bayer CropScience); first registered in 1977 in France. Patents FR 2254276 Manufacturers Bayer CropScience; Sannong
APPLICATIONS
fosetyl-aluminium
Biochemistry Acts by inhibiting germination of spores or by blocking development of mycelium and sporulation. Mode of action Systemic fungicide, rapidly absorbed through the plant leaves or roots, with translocation both acropetally and basipetally. Uses Control of diseases caused by e.g. Phytophthora, Pythium, Plasmopara, Bremia spp., etc. on a variety of crops including vines, fruit (citrus, pineapples, avocados, stone fruit and pome fruit), berries, vegetables, hops, ornamentals and turf. Application rates range from 1-7 kg/ha in citrus, 2 kg/ha in tree nuts, up to 3.6 kg/ha in pome fruit, 2 kg/ha in grapes and 2.4-4.5 kg/ha in cucumber. Also useful activity against several bacterial plant pathogens. Formulation types WG; WP. Compatibility Incompatible with foliar fertilisers. Selected products: 'Aliette' (Bayer CropScience); 'Fosim' (Agrimix); 'Manaus' (Rocca); 'Mikal' (various mixtures) (Bayer CropScience); 'Valete' (Vapco); 'Vialphos' (Vipesco)
OTHER PRODUCTS
fosetyl-aluminium
'Fosbel' (Probelte); 'Fosetal' (Papaeconomou); 'Prudence' (Bayer CropScience); 'Terronate' (Agriliance) mixtures: 'Altigan Flash' (+ folpet) (Sipcam Phyteurop); 'Artimon' (+ mancozeb) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Elicio' (+ fenamidone) (Bayer CropScience); 'Equation System' (+ famoxadone) (DuPont); 'Impresario' (+ famoxadone) (DuPont); 'Mildex' (+ fenamidone) (Bayer CropScience); 'Rhodax Express' (+ mancozeb) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Rhodax M' (+ mancozeb) (Philagro); 'Rhodax' (+ mancozeb) (Bayer CropScience); 'Sillage' (+ metiram) (BASF); 'Tertio' (+ cymoxanil+ fenamidone) (Bayer CropScience); 'Valiant' (+ cymoxanil+ folpet) (Bayer CropScience); 'Verita' (+ fenamidone) (Bayer CropScience) Discontinued products mixtures: 'Carlit' * (+ mancozeb+ benalaxyl) (Aventis); 'Chipco' * (+ iprodione) (Aventis)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by iodometric potentiometric titration (CIPAC Handbook, 1995, G, 82-88). Residues determined by glc of the parent compound and its metabolite. Details of methods are available from Bayer CropScience.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
fosetyl-aluminium
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >7080 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats and rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >5.11 mg/l air. NOEL NOAEL (2 y) for dogs 298 mg/kg b.w. Non-teratogenic and non-mutagenic. ADI 2.98 mg/kg b.w (company proposed) Other Non-carcinogenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) III
ECOTOXICOLOGY
fosetyl-aluminium
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail >8000 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard duck >20 000 ppm diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 428.1, bluegill sunfish 173.2 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) >100 mg/l. Algae EC50 (90 h) for Scenedesmus pannonicus 21.9 mg/l. Bees LD50 (96 h, oral) >461.8 µg/bee; (contact) >1000 µg/bee Worms LC50 (14 d) >1000 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Fosetyl-aluminium is almost completely absorbed and undergoes extensive metabolic transformation. The major end-products, CO2 and phosphorous acid, are excreted in expired air and urine, respectively. Plants The metabolism of fosetyl-aluminium in plants proceeds through the hydrolytic cleavage of the ethyl ester bond. Phosphorous acid is detected as the major metabolite. Soil/Environment In soil, fosetyl-aluminium has an extremely short half-life under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions, with rapid dissipation and metabolism; DT50 (aerobic) 20 min to 1.5 h. In microbially active water/sediment systems, fosetyl-aluminium is rapidly degraded; DT50 14 to 40 h.
|