|
fluometuron
Herbicide
HRAC C2, also F3 WSSA 7, also 13; urea
NOMENCLATURE
Common name fluometuron (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI, WSSA)
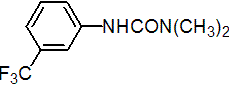
IUPAC name 1,1-dimethyl-3-(a,a,a-trifluoro-m-tolyl)urea
Chemical Abstracts name N,N-dimethyl-N'-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]urea
CAS RN [2164-17-2] EEC no. 218-500-4 Development codes C 2059 (Ciba)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 232.2 M.f. C10H11F3N2O Form White crystals. M.p. 163-164.5 ºC V.p. 0.125 mPa (25 ºC); 0.33 mPa (30 ºC) (OECD 104) KOW logP = 2.38 S.g./density 1.39 at 20 ºC Solubility In water 110 mg/l (20 ºC). In methanol 110, acetone 105, dichloromethane 23, n-octanol 22, hexane 0.17 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Stable in acidic, neutral, and alkaline media at 20 ºC. Decomposed by u.v. irradiation.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by C. J. Counselman et al. (Proc. South Weed Conf., 17th, 1964, 189). Introduced by Ciba AG (now Syngenta AG) and first marketed in the early 1970s. Divested to Makhteshim-Agan in 2001. Patents BE 594227; GB 914779 Manufacturers ÉMV; Griffin; Makhteshim-Agan; Nufarm GmbH; Sannong
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Photosynthetic electron transport inhibitor at the photosystem II receptor site. Also inhibits carotenoid biosynthesis; target enzyme not known. Mode of action Selective systemic herbicide, absorbed more readily by the roots than by the foliage, with translocation acropetally. Uses Control of annual broad-leaved weeds and grasses in cotton and sugar cane, at 1.0-1.5 kg/ha. Phytotoxicity Phytotoxic to sugar beet, beetroot, soya beans, french beans, brassicas, tomatoes, legumes, cucurbits, aubergines, and several other crops. Formulation types SC; WP. Selected products: 'Cotoran' (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Flomet' (Micro Flo); 'Meturon' (Griffin); mixtures: 'Cotolina' (+ trifluralin) (Aragro); 'Cottonex Pro' (+ prometryn) (Aragro)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Cotolint' (Nufarm GmbH); 'Cottonex' (Makhteshim-Agan) mixtures: 'Bandit' (+ prometryn) (Crop Care); 'Command Cotton' (+ clomazone) (FMC); 'Cotogard' (+ prometryn) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Cottonex Com' (+ trifluralin) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Cottonex D' (+ diuron) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Cottonex P' (+ prometryn) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Cottonex PG' (+ glyphosate-isopropylammonium+ prometryn) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Croak' (+ MSMA) (Drexel); 'Double Team' (+ prometryn) (Makhteshim-Agan)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 977.07; CIPAC Handbook, 1983, 1B, 1842) or by hplc (G. W. Sheehan & A. Sobolewski, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1984, 13, 241). Residues determined by hydrolysis to a,a,a-trifluoro-m-toluidine, a derivative of which is measured by glc with ECD (G. Voss et al., ibid., 1973, 7, 569). In water, by lc with u.v. detection (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 992.14).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
IARC ref. 30 class 3 Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >6000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000, rabbits >10 000 mg/kg. Mild skin and eye irritant (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser. NOEL (2 y) for rats 19, mice 1.3 mg/kg b.w. daily; (1 y) for dogs 10 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI 0.013 mg/kg b.w. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) II
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds LD50 for mallard ducks 2974 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for Japanese quail 4620, mallard ducks 4500, ring-necked pheasants 3150 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 30, bluegill sunfish 48, catfish 55, crucian carp 170 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 10 mg/l. Algae EC50 (3 d) 0.16 mg/l. Bees LD50 (oral) >155 mg/bee; (topical) >190 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) for earthworms >1000 mg/kg soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In rats, mainly formation of demethylated metabolites and some conjugation with gluconuronic acid. Elimination, mainly in the urine, was 96% within one week. Plants In plants, degraded by a three-step process, first demethylation to a monomethyl, then to a demethylated intermediate, and finally deamination-decarboxylation to an aniline derivative. Soil/Environment In soil, microbial degradation is significant and rapid, with continual liberation of CO2. Photodecomposition and volatilisation are insignificant. It is moderately leachable in all but very sandy soils: Koc 31-117 (8 soil types); Kd 0.15-1.13. Median DT50 in soil c. 30 d; depending on environmental factors, range was 10 to almost 100 d; dry conditions reduce breakdown.
|