|
diphacinone
Rodenticide
indandione anticoagulant
NOMENCLATURE
Common name diphacinone (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI); diphacins (JMAF); diphenadione (BAN); diphacin (former exception, Turkey); no name (Italy)
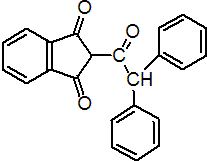
IUPAC name 2-(diphenylacetyl)indan-1,3-dione
Chemical Abstracts name 2-(diphenylacetyl)-1H-indene-1,3(2H)-dione
CAS RN [82-66-6] EEC no. 201-434-5
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is 95% pure. Mol. wt. 340.4 M.f. C23H16O3 Form Yellow crystals; (tech., yellow powder). M.p. 145-147 ºC V.p. 1.37 ´ 10-5 mPa (25 ºC, tech.) KOW logP = 4.27 Henry 1.55 ´ 10-5 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.281 Solubility Practically insoluble in water (c. 0.3 mg/kg). In chloroform 204, toluene 73, xylene 50, acetone 29, ethanol 2.1, heptane 1.8 (all in g/kg). Soluble in alkalis with the formation of salts. Stability Stable for 14 d (pH 6-9); hydrolysed in <24 h (pH 4). Rapidly decomposed in water by sunlight. Decomposes at 338 ºC (without boiling). pKa Acidic, forming water-soluble alkali metal salts.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Rodenticide reported by J. T. Correll et al. (Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med., 1952, 80, 139). Introduced by Velsicol Chemical Corp. (became Novartis Crop Protection AG) and Upjohn Co. (both companies ceased to manufacture and market it). Patents US 2672483 Manufacturers Bell
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Anticoagulant; inhibits the vitamin K-dependent steps in the synthesis of coagulation factors II, VII and X. Mode of action Requires multiple feedings to produce lethal effects. Duration of action much longer than that of warfarin. Uses Control of rats, mice, voles, prairie dogs (Cynomys spp.), ground squirrels, and other rodents. Formulation types CB; RB. Compatibility Chemically and physically compatible with other rodenticides. Selected products: 'Ditrac' (Bell); 'Ramik' (Kemio, HACO)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Promar' (HACO); 'Tomcat' (Antec) Discontinued products: 'Diphacin' * (Velsicol); 'Promer' * (Velsicol); 'Tomcat Rat and Mouse' * (Antec)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc (K. Hunter, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1988, 16, 119, 128). Residues determined by hplc or glc (idem, ibid.).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 2.3, mice 50-300, rabbits 35, cats 14.7, dogs 3-7.5, pigs 150 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats <200 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes; non-sensitising to skin (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats <2 mg/l air (dust). NOEL Chronic LD50 for albino rats is 0.1 mg/kg daily. Other Non-mutagenic in the Ames test. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) Ia; EPA (formulation) I EC classification T+; R28| T; R48/23/24/25
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks 3158 mg/kg. A 56-day secondary poisoning trial with bait (50 mg a.i./kg) revealed no hazard to sparrow hawks under conditions likely to be encountered in nature. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 2.6, bluegill sunfish 7.5, channel catfish 2.1 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 1.8 mg/l.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 175 (WHO, 1995) Animals Not extensively metabolised in the rat; any metabolism mainly involves hydroxylation and conjugation.
|