|
diazinon
Insecticide, acaricide
IRAC 1B; organophosphate
NOMENCLATURE
Common name diazinon (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI, ESA, BAN, JMAF); dimpylate (INN)
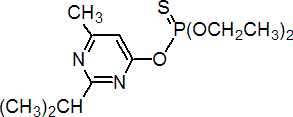
IUPAC name O,O-diethyl O-2-isopropyl-6-methylpyrimidin-4-yl phosphorothioate
Chemical Abstracts name O,O-diethyl O-[6-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl)-4-pyrimidinyl] phosphorothioate
CAS RN [333-41-5] EEC no. 206-373-8 Development codes G 24 480 (Geigy) Official codes OMS 469; ENT 19 507
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is ³95% pure. Mol. wt. 304.3 M.f. C12H21N2O3PS Form Clear colourless liquid; (tech., yellow liquid). B.p. 83-84 ºC/0.0002 mmHg; 125 ºC/1 mmHg V.p. 1.2 ´ 101 mPa (25 ºC) (OECD 104) KOW logP = 3.30 (OECD 107) Henry 6.09 ´ 10-2 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.11 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 60 mg/l (20 ºC). Completely miscible with common organic solvents, e.g. ethers, alcohols, benzene, toluene, hexane, cyclohexane, dichloromethane, acetone, petroleum oils. Stability Susceptible to oxidation above 100 ºC. Stable in neutral media, but slowly hydrolysed in alkaline media, and more rapidly in acidic media; DT50 (20 ºC) 11.77 h (pH 3.1), 185 d (pH 7.4), 6.0 d (pH 10.4). Decomposes above 120 ºC. pKa 2.6 (OECD 112) F.p. ³62 °C
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by R. Gasser (Z. Naturforsch. Teil B, 1953, 8, 225). Introduced in 1953 by J. R. Geigy S.A. (now Syngenta AG). Patents BE 510817; GB 713278 Manufacturers Aako; Agrochem; Cerexagri; Drexel; Hebei Golhil; Hegang Heyou; Hesenta; Makhteshim-Agan; Nippon Kayaku; Sannong; Sudarshan; Sundat; Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Non-systemic insecticide and acaricide with contact, stomach, and respiratory action. Uses Control of sucking and chewing insects and mites on a very wide range of crops, including deciduous fruit trees, citrus fruit, vines, olives, bananas, pineapples, vegetables, potatoes, beet, sugar cane, coffee, cocoa, tea, tobacco, maize, sorghum, alfalfa, flax, cotton, rice, ornamentals, glasshouse crops, forestry, etc., at 300-600 g/ha; soil insects (by soil application); phorid and sciarid flies in mushroom cultivation; flies, lice, mites, fleas, cockroaches, bedbugs, ants, and other insect pests in animal houses and household use. Seed treatment for maize, for control of frit flies and also conferring bird-repellent properties. Also used as a veterinary ectoparasiticide. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic when used as directed. Russetting may occur on green and yellow apple varieties. Formulation types CS; EC; DP; DS; FT; GR; KN; SD; WP; Aerosol; Coating agent. Compatibility Incompatible with copper-containing compounds. Selected products: 'Basudin' (Syngenta); 'Neocidol' (veterinary use) (Syngenta); 'Cekuzinon' (Cequisa); 'Devizinon' (Devidayal); 'Dianon' (Nippon Kayaku); 'Dianozyl' (Agriphar); 'Diazol' (Makhteshim-Agan, AgroSan); 'Efdiazon' (Efthymiadis); 'Knox-out' (Cerexagri); 'Vibasu' (Vipesco); 'Zak' (Kemio)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'DZN' (Syngenta); 'Nucidol' (veterinary use) (Syngenta); 'Agrozon' (Chemvet); 'D-264' (Drexel); 'Diasol' (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Geofos D' (Siapa); 'Granudin' (Agricultura Nacional); 'Kayazinon' (Nippon Kayaku); 'Metazon' (Agrochem); 'Vetazon' (veterinary use) (Chemvet) mixtures: 'Agrox D-L Plus' (+ gamma-HCH+ captan) (Agriliance); 'Agrox Premiere' (+ gamma-HCH+ metalaxyl+ captan) (Agriliance); 'Bipol' (+ permethrin) (Kemio); 'Kernel Guard' (+ gamma-HCH+ captan) (Trace); 'Kick Start' (+ gamma-HCH+ carboxin) (Helena); 'Ondia' (+ benfuracarb) (Otsuka); 'Super Homai' (+ thiophanate-methyl+ thiram) (Nippon Soda); 'Vibaba' (+ fenobucarb) (Vipesco) Discontinued products: 'Kayazol' * (Nippon Kayaku)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc with FID (CIPAC Handbook, 1998, H, 122; Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1972, 6, 345; AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 971.08, 982.06). Residues determined by glc with TID, FPD or MCD, by tlc, by paper chromatography, or by single sweep oscillographic polarography (ibid., 968.24*, 970.33, 970.52, 970.53*; Analyst (London), 1980, 105, 515; Man. Pestic. Residue Anal., 1987, I, 5, 6, S8, S10, S13, S17, S19; Anal. Methods Residues Pestic., 1988, Part I, M2, M5, M12). In drinking water, by glc with NPD (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 991.07).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 68, 70, 92, 94 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 1250, mice 80-135, guinea pigs 250-355 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2150, rabbits 540-650 mg/kg. Not an irritant (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >2330 mg/m3. NOEL (2 y) for rats 0.06 mg/kg b.w.; (1 y) for dogs 0.015 mg/kg b.w. daily, humans 0.02 mg/kg b.w. ADI (JMPR) 0.002 mg/kg b.w. [1993, 2001]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) II or III EC classification Xn; R22| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducklings 2.7, young pheasants 4.3 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 16, rainbow trout 2.6-3.2, carp 7.6-23.4 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.96 mg/l. Algae >1 ppm. Bees Highly toxic to bees. Worms Slightly toxic to earthworms.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 198 (WHO 1998), 63 (WHO, 1986; a general review of organophosphorus insecticides). Animals The principal metabolites are diethyl thiophosphate and diethyl phosphate. Plants Studies with 14C-labelled diazinon show a rapid absorption and translocation in plants. Metabolism proceeds via hydrolysis and subsequent transformation and degradation of the hydroxypyrimidine derivatives to CO2. Soil/Environment Degradation involves oxidation to the phosphate (diazoxon) and hydrolysis (J. Pardue et al., J. Agric. Food Chem., 1970, 18, 405-408). DT50 c. 11-21 d (laboratory). Diazinon is fairly strongly adsorbed onto soil; Kom 332 mg/g o.m. Mobility is low.
|