|
brodifacoum
Rodenticide
coumarin anticoagulant; hydroxycoumarin
NOMENCLATURE
Common name brodifacoum (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI)
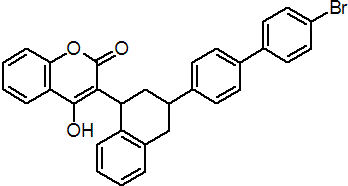
IUPAC name 3-[3-(4'-bromobiphenyl-4-yl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1-naphthyl]-4-hydroxycoumarin
Chemical Abstracts name 3-[3-(4'-bromo-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1-naphthalenyl]-4-hydroxy-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one
CAS RN [56073-10-0] formerly [66052-95-7] EEC no. 259-980-5 Development codes WBA 8119 (Sorex); PP581 (ICI)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. material is >91% pure. Mol. wt. 523.4 M.f. C31H23BrO3 Form White powder; (tech., off-white to buff or beige powder). M.p. 228-232 ºC (tech.) V.p. <<0.001 mPa (20 °C, gas saturation method) KOW logP = 8.5 Henry <1 ´ 10-1 (pH 5.2); <1 ´ 10-3 (pH 7.4); <1 ´ 10-5 (pH 9.3) (all in Pa m3 mol-1, calc.) S.g./density 1.42 (25 °C, tech.) Solubility In water 3.8 ´ 10-3 (pH 5.2), 0.24 (pH 7.4), 10 (pH 9.3) (all in mg/l, 20 °C). In acetone 20, chloroform 3, benzene <6 (all in mg/l, 20 ºC). Stability Thermally (up to 50 ºC) and photolytically (30 d in direct sunlight) stable. Degraded by u.v. light when in solution. pKa A very weak acid which is too lipophilic to form water-soluble salts.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Rodenticide reported by R. Redfern et al. (J. Hyg., 1976, 77, 419). Introduced by Sorex (London) Ltd (now Sorex Ltd) and developed by ICI Agrochemicals (now Syngenta AG). First marketed in 1978. Patents GB 1458670 to Sorex Manufacturers Bell; Sorex; Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibits the vitamin K-dependent steps in synthesis of clotting factors II, VII, IX and X. Mode of action Indirect anticoagulant. Uses Controls most rodent pests, including Rattus norvegicus, R. rattus, Mus musculus and M. domesticus, at lower rates than many other anticoagulants (e.g. warfarin and pindone); also Cricetus cricetus, Mesocricetus auratus, Microtus pennsylvanicus, M. pinetorum, R. argentiventer, R. rattus mindanensis and rodents, such as hamsters, that are difficult to control with other anticoagulants. Potency is such that a rodent may absorb a lethal dose by taking a 50 mg/kg bait as part of its food intake on only one occasion. For a review, see A. P. Buckle & R. H. Smith, "Rodent Pests and their Control", CABI (1994). Formulation types AB; BB; RB. Selected products: 'Brodifacoum Rat & Mouse Bait' (Sorex); 'Klerat' (Sorex); 'Talon' (Sorex); 'Brodi-F' (Trithin); 'Nofar' (Vapco)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Sorexa Checkatube' (Sorex) Discontinued products: 'Havoc' * (Zeneca)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc with u.v. detection (CIPAC Handbook, 1985, 1C, 1981; AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 983.11; Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1988, 16, 134). Residues determined by hplc (idem, ibid.). Details from Syngenta.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 0.4, male rabbits 0.2, male mice 0.4, female guinea pigs 2.8, cats c. 25, dogs 0.25-3.6 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits 0.25-0.63 mg/kg. Slight to mild skin and eye irritant (rabbits). A moderate skin sensitiser (guinea pigs), but negligible risk of sensitisation from formulated product. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for male rats 4.86, female rats 3.95 mg/l air. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) Ia; EPA (formulation) I EC classification T+; R27/28| T; R48/24/25| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for Japanese quail 11.6, chickens 4.5, mallard ducks 0.31 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (40 d) for mallard ducks 2.7, bobwhite quail 0.8 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 0.165, rainbow trout 0.051 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.34 mg a.i./l (as formulation).
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 175 (WHO, 1995). Animals In mammals, a number of hydroxycoumarins are formed. Soil/Environment Degraded in soils (pH 5.5 to pH 8) under aerobic and flooded conditions. Koc (average) 50 000, range 14 000-106 000; Kd 1040 (average), range 625-1320. DT50 >12 w. Unlikely to leach; <2% leached >2 cm in laboratory columns.
|