|
azoxystrobin
Fungicide
FRAC 11, C3; strobilurin type: methoxyacrylate
Synthetic analogue of naturally occurring fungal metabolites the strobilurins and oudemansins.
NOMENCLATURE
Common name azoxystrobin (BSI, pa ISO)
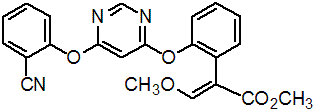
IUPAC name methyl (E)-2-{2-[6-(2-cyanophenoxy)pyrimidin-4-yloxy]phenyl}-3-methoxyacrylate
Chemical Abstracts name methyl (E)-2-[[6-(2-cyanophenoxy)-4-pyrimidinyl]oxy]-a-(methoxymethylene)benzeneacetate
CAS RN [131860-33-8] formerly [215934-32-0] Development codes ICIA5504 (ICI)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 403.4 M.f. C22H17N3O5 Form White solid. M.p. 116 °C; (tech., 114-116 °C) V.p. 1.1 ´ 10-7 mPa (20 °C) KOW logP = 2.5 (20 °C) S.g./density 1.34 (20 °C) Solubility In water 6 mg/l (20 ºC). Low solubility in hexane, n-octanol; moderate solubility in methanol, toluene, acetone; high solubility in ethyl acetate, acetonitrile, dichloromethane. Stability DT50 for aqueous photolysis 2 w. Stable to hydrolysis.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Reported by J. R. Godwin et al. (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1992, 1, 435). Introduced by Zeneca Agrochemicals (now Syngenta AG) and first marketed in 1996. Patents EP 382375 Manufacturers Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibits mitochondrial respiration by blocking electron transfer between cytochrome b and cytochrome c1, at the ubiquinol oxidising site. Controls pathogenic strains resistant to the 14-demethylase inhibitors, phenylamides, dicarboxamides or benzimidazoles. Mode of action Fungicide with protectant, curative, eradicant, translaminar and systemic properties. Inhibits spore germination and mycelial growth, and also shows antisporulant activity. Uses Controls the following pathogens at application rates between 100 to 375 g/ha: Erysiphe graminis, Puccinia spp., Leptosphaeria nodorum, Septoria tritici and Pyrenophora teres on temperate cereals; Pyricularia oryzae and Rhizoctonia solani on rice; Plasmopara viticola and Uncinula necator on vines; Sphaerotheca fuliginea and Pseudoperonospora cubensis on cucurbitaceae; Phytophthora infestans and Alternaria solani on potato and tomato; Mycosphaerella arachidis, Rhizoctonia solani and Sclerotium rolfsii on peanut; Monilinia spp. and Cladosporium carpophilum on peach; Pythium spp. and Rhizoctonia solani on turf; Mycosphaerella spp. on banana; Cladosporium caryigenum on pecan; Elsino?fawcettii, Colletotrichum spp. and Guignardia citricarpa on citrus; Colletotrichum spp. and Hemileia vastatrix on coffee. Phytotoxicity Good crop safety, except on some varieties of apple (e.g. McIntosh, Cox). Formulation types SC; WG.; GR; SE. Selected products: 'Amistar' (not USA) (Syngenta); 'Heritage' (USA, Japan) (Syngenta); 'ZX' (Barclay); mixtures: 'Quadris' (+ cymoxanil) (Syngenta); 'Amistar Admire' (+ imidacloprid) (Bayer CropScience)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Abound' (nuts and fruit) (Syngenta); 'Bankit' (bananas) (Syngenta); 'Gemstone' (Syngenta); 'Olympus' (Syngenta); 'Ortiva' (vegetables) (Syngenta); 'Priori' (vegetables, ornamentals, soya beans, coffee) (Syngenta); 'Landgold Strobilurin 250' (Landgold); 'Protege' (Gustafson) mixtures: 'Amistar Pro' (+ fenpropimorph) (cereals) (Syngenta); 'Amistar Ter' (+ hexaconazole) (cereals, peas) (Syngenta); 'Amistar-Prince' (+ fipronil) (rice nursery box) (Syngenta, Nihon Nohyaku, Nissan); 'Melody Star' (+ iprovalicarb) (Germany, Italy, Portugal) (Bayer CropScience)
ANALYSIS
Residues in water by hplc with fluorescence detection (T. J. Meyers & P. D. Francis, Proc. 9th IUPAC Int. Congr. Pestic. Chem., London (1998), 2, 7C-010).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male and female rats and mice >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Slight eye and skin irritation (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h, nose only) for male rats 0.96, female rats 0.69 mg/l. NOEL (2 y) for rats 18 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI 0.1 mg/kg b.w. (EU); 0.18 mg/kg b.w. (USA) Other Not genotoxic, carcinogenic or neurotoxic; azoxystrobin has no effect on fertility parameters nor on foetal or infant development. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U EC classification T; R23| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail >2000 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5200 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 0.47, bluegill sunfish 1.1, carp 1.6, sheepshead minnow 0.66 mg/l. For degradate R234886, LC50 >150 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) 80 mg/l. EC50 for degradates: R234886 >180, R401553 >50, R402173 >50 mg/l. Algae EC50 (120 h) for Selenastrum capricornutum 0.12 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. LC50 (96 h) for mysid shrimp 55 mg/l; EC50 (48 h) for pacific oyster 1300 mg/l; EC50 (14 d) for Lemna gibba 3.2 mg/l. Bees LD50 for honeybees (oral) >25 mg/bee; (contact) >200 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) for earthworms 283 mg/kg. Other beneficial spp. Harmless to non-target organisms, including predatory mites and bugs, spiders, lacewings, hoverfly, ladybird, carabid beetle, parasitoid wasps and bees, under field conditions at field application rates (IOBC); e.g. LR50 (7 d) for Typhlodromus pyri >1500 g/ha; LR50 (48 h) for Aphidius rhopalosiphi >1135 g/ha.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In rats, the majority of radiolabel is excreted in the faeces, with little remaining radioactivity in any tissues of the animal. A large number of metabolites was formed, of which only the glucuronide of azoxystrobin acid is present at >10% of the administered dose. In goats and hens, azoxystrobin is also excreted rapidly, with low residues in milk, meat or eggs. For details, see R. S. I. Joseph in "Pesticide Chemistry and Bioscience". Plants In wheat, grapes and peanuts, metabolism was extensive, but parent azoxystrobin was the only major (>10%) residue. Metabolism followed similar pathways in all three crops. Soil/Environment Average DT50 (lab.) 8 w (20 °C, pF 2). In soil, in the dark, six identified metabolites were formed; over 1 y, 45% of applied radiolabel is evolved as CO2. Dissipation in the field is faster, average DT50 2 w, DT90 41 w. On soil, photolysis DT50 11 d. Azoxystrobin and its degradates have low to moderate mobility in soil; typical Koc for azoxystrobin c. 500. Field dissipation studies showed that neither azoxystrobin nor its major degradates were typically found in soil below the top 15 cm.
|