|
atrazine
Herbicide
HRAC C1 WSSA 5; 1,3,5-triazine
NOMENCLATURE
Common name atrazine (BSI, E-ISO, (f) F-ISO, ANSI, WSSA, JMAF)
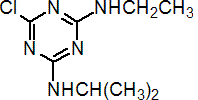
IUPAC name 6-chloro-N2-ethyl-N4-isopropyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine
Chemical Abstracts name 6-chloro-N-ethyl-N'-(1-methylethyl)-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine
CAS RN [1912-24-9] EEC no. 217-617-8 Development codes G 30 027 (Geigy)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is ³96% pure. Mol. wt. 215.7 M.f. C8H14ClN5 Form Colourless powder. M.p. 175.8 ºC B.p. 205.0 °C/101 kPa V.p. 3.85 ´ 10-2 mPa (25 ºC) (OECD 104) KOW logP = 2.5 (25 ºC) Henry 1.5 ´ 10-4 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.23 (22 °C) Solubility In water 33 mg/l (pH 7, 22 ºC). In ethyl acetate 24, acetone 31, dichloromethane 28, ethanol 15, toluene 4.0, n-hexane 0.11, n-octanol 8.7 (all in g/l, 25 ºC). Stability Relatively stable in neutral, weakly acidic and weakly alkaline media. Rapidly hydrolysed to the hydroxy derivative in strong acids and alkalis, and at 70 ºC in neutral media; DT50 (pH 1) 9.5, (pH 5) 86, (pH 13) 5.0 d. pKa 1.7, v. weak base
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by H. Gysin & E. Knüsli (Proc. Int. Congr. Crop Prot., 4th, Hamburg, 1957). Introduced by J. R. Geigy S.A. (now Syngenta AG). Patents BE 540590; GB 814947 Manufacturers Agrochem; Atanor; Crystal; Dow AgroSciences; Drexel; DuPont; Hegang Heyou; Hesenta; Makhteshim-Agan; Meghmani; Nagarjuna Agrichem; Oxon; Rallis; Sannong; Sharda; Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Photosynthetic electron transport inhibitor at the photosystem II receptor site. Maize tolerance is attributed to rapid detoxification by glutathione transferases. Mode of action Selective systemic herbicide, absorbed principally through the roots, but also through the foliage, with translocation acropetally in the xylem and accumulation in the apical meristems and leaves. Uses Pre- and post-emergence control of annual broad-leaved weeds and annual grasses in maize, sorghum, sugar cane, pineapples, chemical fallow, grassland, macadamia nuts, conifers, industrial weed control. In Europe, use is concentrated in maize and sorghum at £1.5 kg/ha. Used also in combinations with many other herbicides. Phytotoxicity Phytotoxic to many crops, including most vegetables, potatoes, soya beans, and peanuts. Formulation types FW; GR; SC; WG; WP. Selected products: 'AAtrex' (USA) (Syngenta); 'Agri-atrazina' (Cequisa); 'Aktikon' (Nitrokémia); 'Atranex' (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Atraplex' (Ingeniería Industrial); 'Atrataf' (Rallis); 'Atratylone' (Agriphar); 'Atrazol' (Sipcam); 'Attack' (Devidayal); 'Coyote' (Milenia); 'Dhanuzine' (Dhanuka); 'Sanazine' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Surya' (Nagarjuna Agrichem); 'Triaflow' (Inquiport); 'Zeazin S 40' (Istrochem); mixtures: 'Bicep II Magnum' (+ benoxacor+ S-metolachlor) (USA) (Syngenta); 'Bicep Magnum' (+ S-metolachlor) (USA) (Syngenta); 'Callisto' (+ mesotrione) (Syngenta); 'Gesaprim' (+ terbutryn) (Europe) (Syngenta); 'Marksman' (+ dicamba-potassium) (Syngenta, BASF); 'Erunit' (+ acetochlor+ AD 67) (Nitrokémia); 'Keystone' (+ dichlormid+ acetochlor) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Trinovin' (+ simazine+ amitrole) (Efthymiadis)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Weedex Liquid' (Syngenta); 'Atradex' (Crop Care); 'Atrazina' (Cequisa); 'Atred' (Chemiplant); 'Azoprim' (Azot); 'Cornazine' (Papaeconomou); 'Crisazina' (Crystal); 'DG90' (Sipcam UK); 'Fogard' (Isagro); 'Gladezine' (Marman); 'Herpazine' (Agrochem); 'Mebazine' (Bayer CropScience); 'Trac' (Atanor); 'Vectal' (Bayer CropScience); 'Zeacas' (CAS) mixtures: 'A-11976E' (+ glyphosate-isopropylammonium) (Syngenta); 'Bicep Magnum TR' (+ flumetsulam+ S-metolachlor) (Syngenta); 'Alazine' (+ alachlor) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Anibal' (+ diuron) (Aragro); 'Aracloro Super' (+ alachlor) (Aragro); 'Aspect' (+ flufenacet) (Bayer CropScience); 'Aterbutex' (+ terbutryn) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Aterbutox' (+ terbutryn) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Athado Invierno' (+ terbumeton+ terbuthylazine) (Probelte); 'Atoll' (+ isoxaflutole) (Bayer CropScience); 'Atramet Combi' (+ ametryn) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Atrasim' (+ simazine) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Axiom AT' (+ flufenacet+ metribuzin) (Bayer CropScience); 'Barko' (+ metosulam) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Basis Gold' (+ nicosulfuron+ rimsulfuron) (DuPont); 'Bellater' (+ cyanazine) (Feinchemie Schwebda); 'Brox-AT' (+ bromoxynil octanoate) (Albaugh); 'Bullet' (+ alachlor) (Monsanto); 'Century' (+ dimethenamid) (BASF); 'Cinch ATZ' (+ S-metolachlor) (USA) (DuPont); 'Clark' (+ bromoxynil octanoate) (Nufarm SA, Syngenta); 'Degree Xtra' (+ acetochlor) (with safener) (Monsanto); 'Field Master' (+ glyphosate-isopropylammonium+ acetochlor) (Monsanto); 'Fogart' (+ simazine) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'FulTime' (+ dichlormid+ acetochlor) (Dow AgroSciences); 'G-Max Lite' (+ dimethenamid-P) (BASF); 'Guardsman Max' (+ dimethenamid-P) (BASF); 'Guardsman' (+ dimethenamid) (BASF); 'Harness Xtra' (+ acetochlor) (Monsanto); 'Karal' (+ bromoxynil) (Nufarm SA); 'Laddok' (+ bentazone-sodium) (BASF, Sipcam); 'Lariat' (+ alachlor) (Monsanto); 'Leadoff' (+ dimethenamid) (DuPont); 'Liberty ATZ' (+ glufosinate-ammonium) (Bayer CropScience); 'Metto' (+ metosulam) (Dow AgroSciences, Bayer CropScience); 'Propachlor Doble' (+ alachlor) (Probelte); 'Ready Master ATZ' (+ glyphosate-isopropylammonium) (Monsanto); 'Sabrine' (+ bromoxynil) (Nufarm SA); 'Shotgun' (+ 2,4-D-2-ethylhexyl) (UAP, Platte); 'Simapron Doble' (+ simazine) (Probelte); 'Simazat' (+ simazine) (Drexel); 'Triamex' (+ simazine) (Bayer CropScience); 'Zeazin Mix DKV' (+ prometryn) (Istrochem); 'Zeazin Mix Extra' (+ metolachlor+ prometryn) (Istrochem) Discontinued products: 'Atratol' * (Ciba); 'Gésaprime' * (Syngenta); 'Primatop' * (Ciba-Geigy); 'Cekuzina T' * (Cequisa); 'Griffex' * (Griffin); 'Hungazin' * (Budapest Chemical); 'Maizina' * (Sipcam); 'Zeapos' * (Sagrochem) mixtures: 'Bicep II' * (+ benoxacor+ metolachlor) (Syngenta); 'Bicep' * (+ metolachlor) (USA) (Syngenta); 'Primagram' * (+ metolachlor) (Novartis); 'Primatol' * (+ prometon) (Ciba-Geigy); 'Primextra II Magnum' * (+ benoxacor+ S-metolachlor) (Syngenta); 'Primextra Safeneur' * (+ benoxacor+ metolachlor) (Syngenta); 'Primextra' * (+ benoxacor+ metolachlor) (Europe) (Novartis); 'Primextra' * (+ S-metolachlor) (Syngenta); 'Sutazine' * (+ butylate) (Syngenta); 'Contour' * (+ imazethapyr-ammonium) (BASF); 'Surpass 100' * (+ dichlormid+ acetochlor) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Vorox(i)Granulat 371' * (+ sebuthylazine+ amitrole) (Spiess)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc with FID (CIPAC Handbook, 1998, H, 33; FAO Specification (CP/61); AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 971.08). Residues determined by glc with ECD or FID (K. Ramsteiner et al., J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1974, 57, 92; E. Knüsli, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1972, 6, 600; B. G. Tweedy & R. A. Kahrs, ibid., 1978, 10, 493). In drinking water, by glc with NPD (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 991.07) or by magnetic particle immunoassay (ibid., 995.08); dealkylated atrazine can be determined by lc with u.v. detection (ibid., 992.14).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
IARC ref. 53, 73 class 3 Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 1869-3090 mg tech./kg, mice >1332-3992 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >3100 mg/kg. Mild skin irritant; non-irritating to eyes (rabbits). Skin sensitiser in guinea pigs, but not in humans. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >5.8 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 10 mg/kg diet (0.5 mg/kg daily), for dogs 150 mg/kg diet (3.75 mg/kg daily), for mice 10 mg/kg diet (1.4 mg/kg daily). ADI 0.005 mg/kg b.w. Water GV 2 mg/l (TDI 0.5 mg/kg b.w.). Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) III EC classification Xn; R48/22| R43| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 varies from 940 mg/kg for bobwhite quail to >2000 mg/kg for mallard ducks and 4237 mg/kg for adult Japanese quail. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for Japanese quail (chicks) >5000, (adults) >1000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 4.5-11.0, bluegill sunfish 16, carp 76, catfish 7.6, guppies 4.3 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 6.9 mg/l. Algae EC50 (72 h) for Scenedesmus subspicatus 0.043 mg/l, (96 h) for Selenastrum capricornutum 0.13 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. Long-term studies in aquatic ecosystems indicate no permanent damage up to 0.020 mg/l. Bees LD50 (oral) >97 mg/bee; (contact) >100 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) for Eisenia foetida 78 mg/kg soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In mammals, following oral administration, atrazine is rapidly and completely metabolised, primarily by oxidative dealkylation of the amino groups (R. Ikonen et al., Toxicol. Lett., 1988, 44, 109; Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 1989, 43, 199; Y. Deng et al., J. Agric. Food Chem., 1990, 38, 1411), and by reaction of the chlorine atom with endogenous thiols. Diaminochlorotriazine is the main primary metabolite, which readily conjugates with glutathione. More than 50% of the dose is eliminated in the urine and around 33% in the faeces within 24 h. Plants In tolerant plants, atrazine is readily metabolised to hydroxyatrazine and amino acid conjugates, with further decomposition of hydroxyatrazine by degradation of the side-chains and hydrolysis of the resulting amino acids on the ring, together with evolution of CO2. In sensitive plants, unaltered atrazine accumulates, leading to chlorosis and death. Soil/Environment Major metabolites under all conditions are desethylatrazine and hydroxyatrazine. Field DT50 16-77 d (median 41 d), the longer values being from cold or dry conditions. In natural waters, DT50 10-105 d (mean 55 d). DT50 under groundwater conditions 105->200 d, depending on test system (M. J. Wood et al. in: A Walker (Ed.), Pesticides in soils and water: current perspectives (BCPC Monograph 1991, 47, 175-182)). Kd 0.2-18 ml/g, Koc 39-173 ml/g; desalkylated metabolites had values similar to those of atrazine, while hydroxyatrazine was much more strongly adsorbed.
|