|
ametryn
Herbicide
HRAC C1 WSSA 5; 1,3,5-triazine
NOMENCLATURE
Common name ametryn (BSI (since 1984), E-ISO, ANSI, WSSA, JMAF); ametryne (BSI (before 1984), (f) F-ISO)
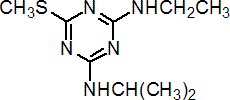
IUPAC name N2-ethyl-N4-isopropyl-6-methylthio-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine
Chemical Abstracts name N-ethyl-N'-(1-methylethyl)-6-(methylthio)-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine
CAS RN [834-12-8] EEC no. 212-634-7 Development codes G 34 162 (Geigy)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition 96% pure. Mol. wt. 227.3 M.f. C9H17N5S Form White powder. M.p. 86.3-87.0 ºC B.p. 337 °C/98.6 kPa V.p. 0.365 mPa (25 ºC) (OECD 104) KOW logP = 2.63 (25 ºC) Henry 4.1 ´ 10-4 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.18 (22 ºC) Solubility In water 200 mg/l (20 ºC). In acetone 610, methanol 510, toluene 470, n-octanol 220, hexane 12 (all in g/l, 25 ºC). Stability Stable in neutral, weakly acidic, and weakly alkaline media. Hydrolysed by strong acids (pH 1) and alkalis (pH 13) to the herbicidally-inactive 6-hydroxy derivative. Slowly decomposed by u.v. light. pKa 4.1, weak base
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by H. Gysin & E. Knüsli (Adv. Pest Control Res., 1960, 3, 289). Introduced by J. R. Geigy S.A. (now Syngenta AG). Patents GB 814948; CH 337019 Manufacturers Atanor; Crystal; Hegang Heyou; Hesenta; Makhteshim-Agan; Oxon; Sannong; Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Photosynthetic electron transport inhibitor at the photosystem II receptor site. Mode of action Selective systemic herbicide, absorbed by the leaves and roots, with translocation acropetally in the xylem, and accumulation in the apical meristems. Uses Pre- and post-emergence control of most annual grasses and broad-leaved weeds in pineapples, sugar cane, bananas, citrus fruit, maize, cassava, coffee, tea, sisal, cocoa, oil palms, and on non-crop land. Application rates are in the range 2-4 kg/ha, except when used as a directed spray on maize. Also used as a potato haulm desiccant. Phytotoxicity Some sugar cane varieties show temporary chlorosis and scorching of lower leaves. Formulation types EC; FW; SC; WG; WP. Selected products: 'Evik' (USA) (Syngenta); 'Gesapax' (Syngenta); 'Ameflow' (Inquiport); 'Amesip' (Sipcam); 'Ametrex' (Makhteshim-Agan); mixtures: 'Krismat' (+ trifloxysulfuron-sodium) (Syngenta)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Crisatrina' (Crystal); 'Mebatryne' (Bayer CropScience); 'Metrimex' (Sipcam) mixtures: 'Codal' (+ prometryn) (Syngenta); 'Ametrex Extra' (+ simazine) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Ametron' (+ diuron) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Amigan' (+ terbutryn) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Atramet Combi' (+ atrazine) (Makhteshim-Agan)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc with FID (CIPAC Handbook, 1998, H, 22; FAO Specification CP/61; AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 971.08). Residues determined by glc (K. Ramsteiner et al., J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1974, 57, 192; E. Knüsli, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul. Food Addit., 1964, 4, 13; B. G. Tweedy & R. A. Kahrs, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1978, 10, 493). In drinking water, by glc with NPD; AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 991.07.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews J. Pest. Sci., 18(4), 1993 (in Japanese). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 1160 mg tech./kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2020, rats >3100 mg/kg. Not a skin or eye irritant (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >5170 mg/m3 air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 50, for mice 10 ppm; (1 y) for dogs 200 ppm. ADI 0.015 mg/kg. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) III EC classification Xn; R22| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds LC50 (5 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5620 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 5, bluegill sunfish 19, channel catfish 25 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (96 h) 28 mg/l. Algae EC50 (7 d) for Selenastrum capricornutum 0.0036 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. LC50 (96 h) for mysid shrimp (Mysidopsis bahia) 2.3 mg/l. Bees Low toxicity to bees; LD50 (oral) >100 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) for earthworms 166 mg/kg soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Irrespective of the dose or the dosing regime, most is excreted within 3 to 4 days. Conjugation with glutathione and dealkylation are the main metabolic pathways. Plants Metabolised by tolerant plants and, to a lesser extent, by sensitive plants, to non-toxic substances by replacement of the methylthio group by a hydroxy group, and by dealkylation of the amino groups. Soil/Environment Loss from soil is principally by microbial degradation (H. O. Esser et al., Herbicides: Chemistry, Degradation and Mode of Action, 1975, 1, 129). Median DT50 in soil 51 d (11-120 d). Koc 300; however column leaching studies indicate ametryn does not leach significantly. Degradation in aquatic systems is caused by microbial processes, with photolysis also contributing. Adsorption to the sediment is the most efficient mechanism of elimination of ametryn from water.
|